By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that forms in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s anti-microbial network. The lymphatic system consists of lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland and bone marrow. Cancer of the lymph nodes can affect all those areas as well as other parts of the body.
There are different types of lymphoma. The main subgroups are:
• Hodgkin’s lymphoma (which was also called Hodgkin’s disease in the past)
• Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Lymph nodes are small glands in the body that are part of the immune system. You’ve probably heard of lymph nodes, which may have been associated with a cancer diagnosis, but everyone has them and they play an important role in keeping us healthy. Scientifically, lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system, which form a network of body organs, vessels and glands throughout the body. These glands trap bacteria, viruses and other invaders before they can lead to infection. Lymph nodes also are responsible for controlling the circulation of lymph fluid and delivering white blood cells to different parts of the body. (Similar to blood circulation in the veins).
Lymph nodes are concentrated in the neck, under the chin, under the armpits and around the groin, and you may notice swelling of these glands if you are fighting an infection in one of the body parts. These glands, which exist in the body of all humans, play an important role in human health as part of the body’s immune system by fighting infections and filtering bacteria and cancer cells. Lymph nodes are also responsible for managing the flow of lymph fluid and transporting white blood cells to different parts of the body. The lymphatic system is a network of low-pressure vessels throughout the body. These vessels are called lymphatic vessels. In addition to performing important immune functions in the body, the lymphatic system creates a path for the return of intercellular fluids to the circulatory system through the lymphatic vessels. Liquids that flow like blood throughout the lymphatic tissues of the body are called lymph or lymphatic fluid. The lymphatic system also facilitates the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the digestive system.
Glands or lymph nodes destroy foreign cancers and fight infections in the body by destroying the cells associated with the infection through the use of white blood cells in their lymph fluid. Therefore, part of the body’s immune system cells is transferred to the lymph nodes to fight any type of disease. To put it more simply, the lymph node, as part of the immune system, is responsible for defending the body. The multiplicity of cells, in the fight against the factors of infection and cancer, causes swelling of the lymph node or gland.
Swollen Lymph Nodes:
When there is a problem in the body such as an infection, injury, or cancer, the lymph nodes in the affected area may become swollen or enlarged. Because they are working to filter abnormal cells. Swollen lymph nodes give you a sign that something is not working right in the body, but it is other, more specific symptoms that indicate the root of the problem. For example, swollen lymph nodes near the ear plus ear pain and fever are signs that you may have an ear infection or a cold.
There are some areas of the body such as the neck, groin and armpits that generally have large lymph nodes. In most cases, only the lymph nodes in one area are swollen. When the lymph nodes are swollen in more than one area, it is called generalized lymphadenopathy. Some infections, such as streptococcus of throat and chicken pox, infection caused by the use of certain drugs, diseases related to the body’s immune system, and cancers such as lymphoma and leukemia can cause these multiple swellings. Your treating doctor needs more symptoms than swollen lymph nodes to be able to find the root of the problem.
Note:
Swollen lymph nodes are often caused by diseases other than cancer.
Pathophysiology of Lymph Node Cancer:
Cancer can spread from where it started to other parts of the body. When cancer cells break away from their original tumor, they can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. If these cells move through the lymphatic system, cancer cells can also enter the lymph nodes. Most cancer cells escape, die, or are killed before they can start growing and multiplying elsewhere. But it is always possible that one or two cells can escape and settle in new places, grow and form new tumors. The spread of cancer to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, it often enters the lymph nodes near the area of the cancerous tumor. These are the lymph nodes that do the most anti-cancer activity to filter and kill cancer cells.
Risk factors:
Factors that can increase the risk of developing lymphoma include:
• Age. Some types of lymphoma are more common in young adults, while others are more often diagnosed in people over 55.
• Being a man. Men are slightly more likely to develop lymphoma than women.
• Immune system disorder. Lymphoma is more common in people with immune system diseases or in people taking immunosuppressive drugs.
• Occurrence of certain infections. Certain infections are associated with an increased risk of developing lymphoma, including Ebstein-Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Signs and Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of lymphoma may include:
• Painless Swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpit or groin (cancer of the neck lymph nodes, cancer of the axillary lymph nodes or cancer of the groin lymph nodes)
• Constant Fatigue
• Fever
• Night Sweats
• Shortness of Breath
• Unexplained Weight Loss
• Skin ItchingKidney cancer is actually a cancer that starts in the kidneys. Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs. They are located behind your abdominal organs. So, there is a kidney on each side of your spine.
In adults, renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer. Other less common types of kidney cancer may occur. Children are more likely to develop a type of kidney cancer called Wilms’ tumor.
It seems that the incidence of kidney cancer may be increasing. One of the reasons may be the fact that imaging techniques such as computed tomography scan is used more often. These tests may lead to the incidental discovery of more kidney cancers. Kidney cancer is often discovered in the early stages, when the cancer is small and confined to the kidney.
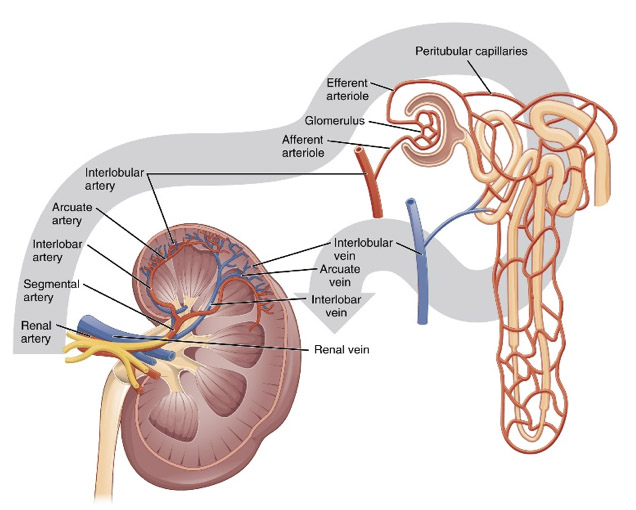
Among the responsibilities of the kidneys are filtering minerals from the blood, maintaining the balance of all fluids in the body, removing waste materials and regulating blood volume. Each kidney is about 4 to 5 inches long. The job of the kidneys is to purify the blood. Kidneys remove waste, control the balance of fluids in the body and keep electrolytes at the right level. During a day, all the blood in the body passes through the kidneys several times. Blood enters the kidney, waste is separated from it, and if necessary, its salt, water and minerals are adjusted. Purified blood is returned to the body circulation. The waste is converted into urine and accumulates in the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped structure that is connected to the bladder with a tube called the ureter and transfers urine to the bladder through the ureters. Each kidney has about a million small filters called nephrons.
If the blood flow to the kidney stops, all or part of the kidney may die, which may lead to kidney failure. Kidneys are located on both sides of the spine, in the retroperitoneal area (under the ribs and behind the abdomen). Due to the location and shape of the liver above the right kidney, the right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney.
Causes of Kidney Cancer:
It is not yet known exactly what factors cause kidney cancer. Doctors know that kidney cancer starts when some kidney cells make changes or mutations in themselves.
A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do. These changes tell the cells to grow and divide faster. Accumulated abnormal cells form a tumor that can spread beyond the kidney. Some cells can spread to distant parts of the body.
Risk Factors:
Factors that can increase the risk of kidney cancer include:
Older Age: The risk of developing kidney cancer increases with age.
Smoking: Smokers have a higher risk of kidney cancer than non-smokers. After quitting, the risk of danger also decreases.
Obesity:
People who are obese have a higher risk of developing kidney cancer than people who are at a healthy weight.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): High blood pressure increases the risk of developing kidney cancer.
Kidney Failure:
People who receive long-term dialysis to treat chronic kidney failure have a higher risk of developing kidney cancer.
Some Hereditary Syndromes:
People who are born with certain hereditary syndromes may have a higher risk of developing kidney cancer. Such as people with von Hippel-Lindau disease, tuberous sclerosis complex, hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma, or familial renal cancer.
Family History of Kidney Cancer: If a person’s first degree relatives have this disease, the risk of developing kidney cancer is higher.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Cancer:
The signs and symptoms of kidney cancer that doctors warn people about have changed dramatically in recent years. The most common symptoms are anemia, fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite and fever.
In the early stages of kidney cancer, there are usually few symptoms, and many diagnoses are made based on laboratory and imaging tests before symptoms appear.
Anemia:
Anemia has many reasons. It also could be is the most common symptom of kidney cancer, and anemia is present in 20-40% of people diagnosed with kidney cancer. The kidneys make a protein called erythropoietin, which causes the bone marrow to produce red blood cells (in a process called erythropoiesis). With kidney cancer, a decrease in the production of this protein leads to a low number of red blood cells (anemia). Conversely, some people may instead have a significant red blood cell (erythrocyte) count due to increased production of erythropoietin by kidney cancer cells. These symptoms are called paraneoplastic syndrome, which occurs due to the presence of substances or hormones produced by cancer cells.
Blood in the urine (Hematuria): It could be one of the common symptoms of kidney cancer that occurs in at least half of the people who are diagnosed with kidney cancer.
The urine may be completely bloody (called gross hematuria), or it may be mild, causing only a pink color in the urine, or it may be microscopic.
Flank Pain: pain may occur in the back side or abdomen and can vary from mild pain to a sharp and throbbing pain. Flank pain that occurs without injury should always be investigated.
Approximately 40% of kidney cancer sufferers experience pain during the course of the disease, but flank pain is less common as a symptom of this disease. It could be as a result of kidney stone or pyelonephritis.
Flank mass (back, side or abdomen):
In some studies, a flank mass (a mass in the back, waist or abdomen) has been found in some of kidney cancer patients. Any mass in this area, even if you assume that it is one of the common fat tumors that appear with age, should be examined by a doctor.
Unintentional weight loss:
Unintentional weight loss is a common symptom of cancer that occurs in about a third of people at the time of diagnosis, which refers to the loss of 5% or more of body weight over a period of 6 to 12 months without changing diet or exercise, is considered unexpected or unintentional weight loss. In addition to kidney cancer, there are a number of other serious diseases associated with this weight loss, and people should always seek medical attention immediately with unwanted weight loss.
Fatigue:
Fatigue also can occur in some people who have kidney cancer. Fatigue related to cancer, unlike normal fatigue, can be profound and usually worsens over time. This type of fatigue is not cured by a good night’s sleep or a decent cup of coffee.
Cachexia:
Cachexia is a syndrome characterized by weight loss, loss of appetite and loss of muscle mass. It needs your doctor’s attention if present.
Loss of Appetite:
Loss of appetite, with or without cachexia, with unwanted weight loss is a common symptom.
To Be Continued