By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Side effects of esophageal cancer:
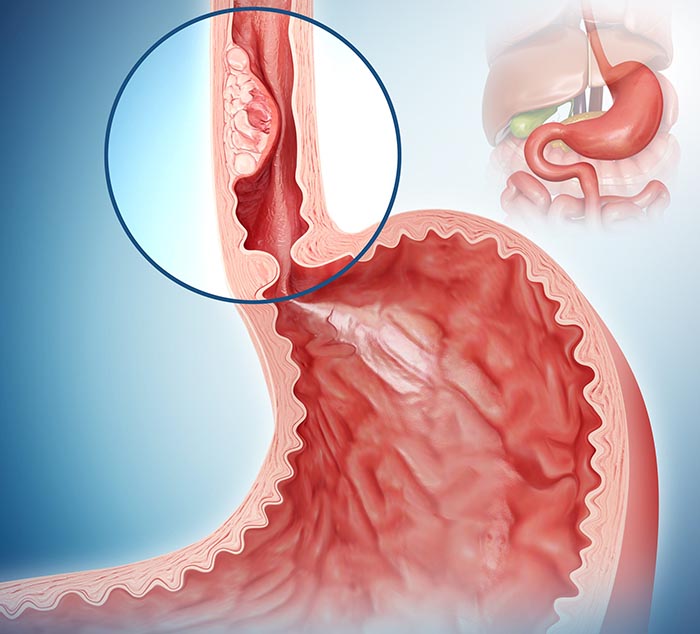
Esophageal cancer can be accompanied by some side effects. Some of them occur due to local involvement such as narrowing or erosion of the esophagus and others due to tumor spread. Common side effects of esophageal cancer include the following:
Esophageal obstruction: Esophageal obstruction is one of the most common complications. For many patients with esophageal cancer in late stages, placement of an esophageal stent is necessary to allow food intake.
Tracheoesophageal fistula: Due to tumor invasion and inflammation, a fistula (abnormal passage) may form between the esophagus and trachea. When this condition occurs, what enters the esophagus can go directly into the trachea and then to the lungs. Tracheoesophageal fistula usually causes coughing when swallowing and chest pain. Treatment may include stent placement in the esophagus and/or trachea. Newer techniques, such as placement of umbrella-shaped valves in the bronchus, may also be considered.
Aortoesophageal Fistula: An uncommon but life-threatening condition that occurs due to the formation of a fistula between the esophagus and the aorta, a large blood vessel that carries blood from the head to the rest of the body. These conditions usually develop in the final stages of the disease, and its symptoms include bleeding from the mouth and pain in the middle of the chest. If diagnosed quickly, surgery may correct the problem.
Aspiration pneumonia: choking sensation while eating or a fistula often causes the contents of the esophagus and stomach to enter the lungs. This condition can lead to aspiration pneumonia, a condition that usually requires hospitalization and antibiotic treatment.
Bleeding: Heavy bleeding may occur from an esophageal ulcer or perforation or as a side effect of stenting. Treatment options depend on the condition and may include cauterizing the bleeding vessels.
Malnutrition: A very common complication of esophageal cancer is malnutrition, which occurs due to a person’s reduced ability to eat. These conditions may require tube feeding to provide the nutrients the body needs.
Causes of esophageal cancer: A cancerous tumor develops from an abnormal cell. The exact reason why a cell becomes cancerous is not known. In this regard, it is believed that some damages or specific changes in the genes of a cell cause this problem. This problem causes the cell to become abnormal and its proliferation out of control. In many people, esophageal cancer develops for no apparent reason. However, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing esophageal cancer, which include the following:
– Age: This type of cancer is more common among older people. Most cases of this disease are among people over 50 years old. This type of cancer is also seen more common among men.
– Nutrition: Diet is probably an effective factor in developing this disease. Diets high in fat can possibly increase the risk of developing the disease, and consuming large amounts of fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk of developing the disease. A person’s obesity can also increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
– Smoking
-Stomach acid return (gastric reflux):
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is observed in some people normally and can cause inflammation of the end of the esophagus. However, it should be noted that the probability of getting cancer due to this problem if left untreated is low and this problem does not cause cancer in most cases but it should be considered.
• Biopsy or Sampling: Your doctor may use a special scope and insert it into your esophagus to take a sample of suspected cancer tissue (sampling). This tissue sample is then sent to the laboratory to determine the presence of any cancer cells.
Stages of disease progression: Once a person is diagnosed with esophageal cancer, your doctor will try to determine the extent (stage) of the cancer in the patient’s body. Doing this can greatly help in determining the treatment method for esophageal cancer. Tests used to detect the stage of cancer progression include CT scan and positron emission tomography (PET). The stages of esophageal cancer progression include the following:
Step I: This stage of cancer is observed in the surface layers of the patient’s esophagus cells.
Step II: This stage of cancer has penetrated into the deeper layers of the esophagus and can also affect the lymph nodes near the esophagus.
Step III: This stage of cancer penetrates into the deepest layers of the esophagus wall and affects the patient’s tissues or lymph nodes.
Step IV: At this stage, cancer cells spread to other parts of the patient’s body.
Diagnosis: Tests and methods used to diagnose esophageal cancer include the following:
• Endoscopy: During an endoscopy, the doctor passes a hollow tube equipped with a camera (scope) down your throat and into your esophagus. Using endoscopy, the doctor examines the condition of your esophageal tissue and looks for areas that are cancerous or inflamed.
– Having Barrett’s esophagus: The term Barrett’s esophagus refers to a disease in which the cells at the end of the esophagus undergo changes. In many cases, this problem is related to the long-term inflammation of these cells as a result of chronic gastric acid reflux that left untreated.