By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Types of small bowel cancer: Like most cancers, small bowel cancer occurs when defective or mutated cells get out of control and form a tumor. This cancer usually starts in the lining of the small intestine and may spread to other parts of the body. Often, this cancer develops in the duodenum or the upper part of this organ. The main types of small bowel cancer are:
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of small bowel cancer that usually develops in the cells of the small bowel wall. Often, this type of cancer is caused by the growth of non-cancerous and benign polyps.
Sarcoma is a type of small intestine cancer that develops in the connective tissue of the small intestine.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are types of soft tissue sarcomas.
Carcinoid tumors that develop in the lining of the intestine and are often slow growing.
Lymphomas are a disease of the immune system that may originate in the intestines.
Causes of small bowel cancer:
Lifestyle and health factors can increase the risk of developing this disease.
Small bowel cancer risk factors include the following:
• Old age
• High-fat diet
• smoking
• Having Crohn’s disease
• Having celiac disease
• Family history of gastrointestinal disorders including hereditary disorders such as familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer.
Signs and symptoms of small bowel cancer:
The early stages of small bowel cancer are often not associated with any signs and symptoms or have symptoms that are commonly observed in other diseases. Most small bowel cancers are diagnosed very late and in the advanced stages of the disease. Some common symptoms of small bowel adenocarcinoma may include:
• Blood in the stool or on the toilet paper
• Unexplained weight loss
• Mass in the abdomen
• Pain, cramping, or swelling in the middle of the abdomen
• Anemia (low number of red blood cells)
• Nausea and vomiting
If you experience any of these symptoms or are concerned, please contact your doctor.
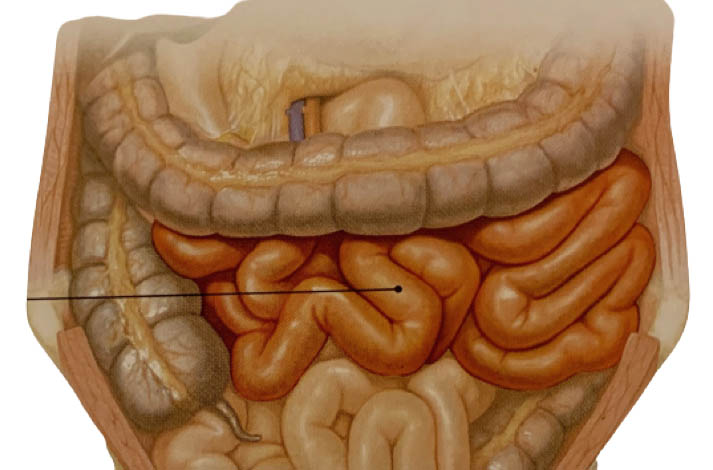
Small bowel cancer is a rare type of cancer that occurs when cancerous cells grow in the tissue of the small intestine. The small intestine is part of the body’s digestive system and it is a long tube that connects the stomach to the large intestine. The role of the small intestine is to absorb most of the nutrients and minerals in food. Over time, small bowel cancer may grow and block the small intestine. The most common type of small bowel cancer is carcinoid tumor, followed by adenocarcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma of the small intestine begins in the glandular cells that are present in the lining of the small intestine and are responsible for making and releasing mucus. Most of these tumors occur in the small intestine near the stomach. Uncommon types of this cancer include sarcoma, lymphoma and gastrointestinal tumors.
Types of small bowel cancer:
Like most cancers, small bowel cancer occurs when defective or mutated cells get out of control and form a tumor. This cancer usually starts in the lining of the small intestine and may spread to other parts of the body. Often, this cancer develops in the duodenum or the upper part of this organ. The main types of small bowel cancer are:
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of small bowel cancer that usually develops in the cells of the small bowel wall. Often, this type of cancer is caused by the growth of non-cancerous and benign polyps.
Sarcoma is a type of small intestine cancer that develops in the connective tissue of the small intestine.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are types of soft tissue sarcoma.
Carcinoid tumors that develop in the lining of the intestine and are often slow growing.
Lymphomas are a disease of the immune system that may originate in the intestines.
Causes of small bowel cancer:
Lifestyle and health factors can increase the risk of developing this disease. Small bowel cancer risk factors include but not limited to the following:
• Old age
• High fat diet
• Smoking
• Having Crohn’s disease
• Having Celiac disease
• Family history of gastrointestinal disorders including hereditary disorders such as familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer.
Having these risk factors doesn’t mean that person get the cancer. It just increase the risk of getting that cancer.
Prevention of small bowel cancer:
Avoiding risk factors can help reduce the risk of developing this type of cancer. Protective measures including physical activity and maintaining body weight can be effective in this direction. Lifestyle changes such as eating a high-fiber diet, eating fresh fruits and vegetables, and cutting down on processed meat are important.
Diagnosis of small bowel cancer:
Accurate diagnosis of this cancer is the first step to prepare a treatment plan for this disease. There are different types of tests and tools to diagnose small bowel cancer, evaluate the disease and develop a treatment plan. During treatment, laboratory tests and imaging will be used to track the size of the tumors and check the response status to treatment. Common tools for diagnosing this cancer and staging the disease include the following:
An upper gastrointestinal x-rays series is a series of x-rays of the esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine. This procedure may require the patient to ingest barium to enhance the X-ray images. If the doctor discovers abnormal cells during this procedure, the next step may be an endoscopy procedure or another diagnostic imaging test for cancer.
Enteroclysis is a test to diagnose this cancer and provides the medical team with more detailed images of the small intestine than an upper gastrointestinal tract exam.
A barium enema is done by inserting barium into the colon and filling the colon. X-rays are enhanced by barium during the enema, enabling the doctor to better identify polyps and other suspicious tissue that may require closer examination or removal during a colonoscopy.
A CT scan is a procedure that provides the doctor with more detailed images of the colon and small intestine. An advanced 4D scanner may help diagnose small bowel cancer.
Endoscopy is a process that allows the doctor to examine the condition inside the esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine. In this method, a tool called an endoscope is used, which usually has a light attached to it and is inserted directly into the cavity or organ of the body.