By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Lung cancer, as one of the deadliest types of cancer in the world, kills a large number of men and women every year. Lung cancer is the second leading cause of death for women in the world after breast cancer. Lung cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the lung tissues. It is worth mentioning that if this disease is not treated, the cell growth can spread outside the lung in a process called metastasis and reach the surrounding tissues or other body organs. The main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Lungs are the center of our respiratory system. Individual human cells need fresh oxygen to survive, and the body must discharge the carbon dioxide that enters the body through the breath to meet the vital needs of the cells. This operation is performed by a pair of spongy and cone-shaped organs located on both sides of the human chest. Lungs are the driving engine of gasification operation to cells and play the main role in breathing and blood circulation. If, for any reason, the lungs cannot carry out gas exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide, the function of other parts and organs of the body will also be disturbed. Therefore, when a part of the lung is damaged, in order to prevent poisoning of the body due to carbon dioxide congestion, the use of a breathing aid is prescribed. In the following, we will take a closer look at this complex system.
Anatomy and Physiology of Lungs:
As mentioned earlier, every human body has two lungs on both sides of the chest, the right lung consists of three lobes and the left lung consists of two lobes. The left side of the chest has one less lobe in order to have enough space to contain the heart. To draw the anatomy of the lung, it is better to say that every human has a tree in the shape of an inverted Y in the chest. As a result of inhaling and exhaling, air is taken to the lungs through the trachea and exits from it.
The oxygen brought in by the trachea is taken by the bronchi into the lungs and the carbon dioxide is returned to the trachea to leave the body. Each bronchial tube is divided into smaller, very fine tubes called bronchioles that extend throughout the lung. The number of bronchioles in each lung reaches 30,000. Each of the bronchioles reach air sacs called alveoli at the end of their path. The existence of 600 million alveoli in the human lung is due to the fact that enough oxygen reaches the cells of the body.
Researchers have divided the respiratory system of the human body into two general parts, the upper respiratory system and the lower respiratory system. According to this classification, the upper respiratory system consists of the following:
Mouth and Nose: In the first stage, fresh oxygen enters the body through the oral cavity and nasal passages.
Nasal Cavity: Oxygen absorbed through the nostrils enters the nasal cavity.
Pharynx: Air swallowed through the mouth enters the pharynx.
Larynx: At the last stage, air enters the last part of the throat, the larynx, to enter the lungs.
The main organs of the respiratory system which are the lungs located in the lower respiratory system. The Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles, alveoli and even the ribs around the lungs and the diaphragm muscles that cause the lungs to expand and contract during breathing also form other components of the lower respiratory system.
Air reaches the end of the throat through the mouth or nose and follows the path of the trachea. The trachea delivers the incoming air to the left or right bronchi. Bronchi divide the air between smaller bronchioles, and a multitude of bronchioles each deliver oxygen to the alveoli according to their task. Here the exchange of oxygen with carbon dioxide takes place. The surface of the alveoli is covered by blood capillaries. The heart sends the blood that contains carbon dioxide to the lungs, the alveoli take the carbon dioxide and delivers the harmful gas to the mouth and nose in the same way that it received the fresh air to leave the body. On the other hand, the alveoli supply oxygen to the blood and returns it to the heart.
The path of a breath proves that if the lungs do not work properly, the volume of carbon dioxide in the body increases and may have consequences such as headache, dizziness, boredom, stroke and even coma. That’s why doctors prescribe ventilators for some patients whose lungs do not perform ventilation operations properly.
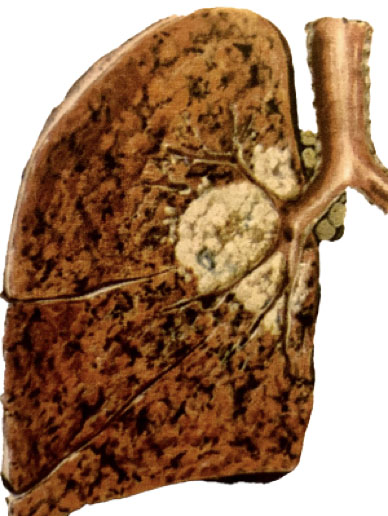
Lung cancer is a disease that causes excessive proliferation of lung tissue cells and reduces a person’s ability to breathe. The lung is a vital organ for breathing and gas exchange, which is located in the chest, and during breathing, it absorbs oxygen from the incoming air and expels carbon dioxide. Normally, the body controls and balances the growth of cells, and cells die at a certain stage of their life cycle to prevent their excessive growth. Cancer disrupts the regulation and balance system of cell growth and leads to the proliferation and excessive division of cells, which eventually creates a mass called a tumor. In lung cancer, this pattern of cellular overgrowth is seen in the lungs. Early diagnosis of lung cancer can be effective in the treatment process, however, it is difficult to identify this cancer in the early stages, because its symptoms are similar to a respiratory infection, and sometimes a person has no symptoms, which is why the prognosis of lung carcinoma is poor. Symptoms of lung cancer include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, pain, fluid accumulation in the lungs, and metastasis to other organs.
Risk Factors:
• Smoking: Doctors believe that the risk of developing lung cancer increases with the number of cigarettes consumed per day and the number of years a person has smoked. Not all smokers get lung cancer, and not all people who develop lung cancer are smokers. But there is no doubt that smoking is one of the biggest risk factors. Quitting smoking at any age significantly reduces the risk of lung cancer. Not only smoking, but also the use of pipes, cigars and other tobacco products such as hookah, cause lung cancer. Tissue changes begin immediately when cigarette smoke, which is full of carcinogens, enters the lungs. These carcinogens are transported through the blood to all parts of the body and the risk of other cancers increases. At first, the body repairs the damage, but with repeated exposure to cigarette smoke, the normal lung cells are increasingly damaged and eventually cancer develops.
• Exposure to Cigarette Smoke: It is interesting to know that even if you do not smoke, exposure to cigarette smoke also increases the risk of developing lung cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, secondhand smoke exposure is responsible for thousands lung cancer deaths in the United States each year.
• Family History of Lung Cancer: The presence of this cancer in first-degree family members such as parents, siblings, increases the possibility of contracting this disease.
• Age: Lung cancer is a disease of the elderly; Almost 70% of people with it are over 65 years old (median age for lung carcinoma is 70), while less than 3% of cases of lung cancer occur in people under 45.
• Air pollution: Air pollution caused by vehicles, industrial equipment and power plants can cause lung cancer in people at risk.
Other Causes of Lung Cancer: In addition to cigarette smoke and air pollution, which are considered to be the main causes of this type of cancer, other factors can affect the development of lung cancer:
• Lung Diseases: the existence of some lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) increase the risk of lung cancer. Having pulmonary fibrosis is also associated with an increase in the risk of lung cancer.
• Exposure to Asbestos and other Carcinogenic Substances: Exposure to asbestos and other substances that cause cancer such as arsenic, cadmium, chromium, nickel, some petroleum products and uranium increases the risk of lung cancer. A type of this cancer called mesothelioma is affected by exposure to asbestos.
• Exposure to Radon Gas: Radon is produced naturally from the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water, and eventually becomes part of the breathing air. The accumulation of radon in the building causes its dangerous levels to appear.
• Exposure to Diesel Engine Fumes: The exhaust fumes from diesel engines include gas and soot (suspended particles). Many occupations, such as truck drivers, toll booth workers, heavy machinery operators, railway and dock workers, miners, garage workers and mechanics, and farm workers often deal with diesel machinery. Studies show that people exposed to diesel car fumes have a small but significant increased risk of lung cancer.
To be continued














