By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Colorectal cancer (Part II):
Who is at risk of colon cancer?
Many people do not know how much they are at risk of colon cancer. So let’s first overview the factors that increase people’s chances of getting colon cancer. Any factor that increases the chance of developing a disease is called a risk factor that it is good to know about. The risk factors for colon cancer include:
۱- Age of 50 years or older:
aging is considered the most important risk factor. The risk of colon cancer increases with age, so that colon cancer occurs in almost two-thirds of cases in people aged 50 years or older.
۲- History of colon polyps
۳- History of colon cancer in first-degree relatives (father, mother, brother, sister, child) at the age of less than 60 years
۴- History of colon precancerous polyps in first degree relatives (father, mother, brother, sister, child) at the age of less than 60 years
۵- Personal history of inflammatory bowel diseases (Ulcerative Colitis or Crohn’s)
۶- Genetics:
the hereditary background of colon cancer exists in various forms, the most important of which are hereditary polyposis syndrome and familial non-polyposis colon cancer (Lynch syndrome).
۷- Unhealthy lifestyle that includes the use of tobacco and drugs or their derivatives (cigarettes, hookah or opium,…), drinking alcohol, unhealthy diet (high consumption of red meat, prepared or fast food, low consumption of vegetables and fresh fruit) and inactivity.
۸- Obesity
۹- Diabetes
۱۰- Fatty liver
Prevention and treatment of colon cancer:
Currently, colon cancer is the second deadliest cancer and the third most common cancer in the world, and it often occurs in people over 50 years of age. Developed countries have been able to reduce more than 40% of deaths from this cancer by implementing screening programs in the last two decades! Colon cancer is not limited to a specific race and it is a threat to the health of all races. Although this disease is slightly more common in men than women, the fact is that both men and women are at risk of colon cancer.
Fortunately, colon cancer is one of the few cancers that can be significantly controlled with screening, early diagnosis and timely treatment. Basically, screening programs target apparently healthy people without specific health problems. This point is important because colon cancer usually progresses slowly and quietly in its early stages and may cause symptoms in advanced stages, in which case it will be more difficult to control and treat. Therefore, the golden time to screen for this disease is the stage before symptoms appear. Also, early detection and removal of colon polyps is a vital thing in preventing this cancer, and with this, the chances of curing the disease increases by 90%.
Diagnosis:
– Screening for colon cancer:
Doctors recommend certain screening tests for healthy people without signs or symptoms to look for colon cancer. Finding colon cancer in its earliest stages provides the greatest chance of cure.
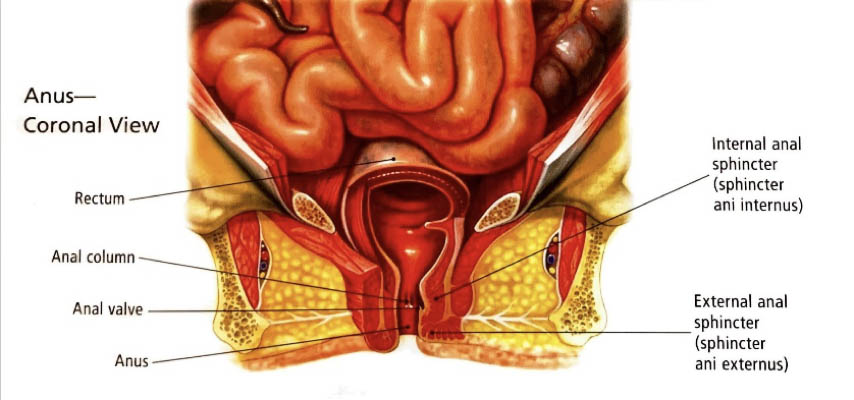
– Colonoscopy:
If signs and symptoms suggest that a person may have colon cancer, the doctor may perform one or more tests, including a colonoscopy. A colonoscopy is performed using a long, flexible, narrow tube connected to a video camera and monitor to view the entire bowel. If a suspicious area is found, doctor can take a sample (biopsy).
-Blood Test:
Usually colon cancer is not detected directly by blood test. But doctor may test blood for clues about patient’s overall health, such as kidney and liver function tests. The doctor may also test the blood for a chemical that is sometimes produced by colon cancer (carcinoembryonic antigen, or CEA). But chronic iron deficiency anemia can be a sign of malignancy.
– Proctoscopy:
In this method, the inside of the rectum and the lower parts of the large intestine are observed directly through special devices. Through this method, half of cancers can be detected. In this method, the patient may feel pressure, discomfort or pain.
– Biopsy:
If there is any mass along these parts or abnormalities, a part of the mass needs to be removed to be examined under a microscope for the presence of cancer tissue or cells.
– Genetic counseling:
Genetic testing and counseling is recommended in families that have a hereditary possibility of colon cancer such as non-polyp colon cancer or familial glandular polyp. Because colon and rectal cancer is insidious, screening is the solution to early detection. Colonoscopy should be done every 10 years in most people who reach the age of 50.
Stage of colon cancer:
Stage I:
Cancer has invaded the surface lining (mucosa) of the colon, but has not spread beyond the bowel wall.
Stage II:
Cancer has spread into the colon wall, but has not invaded the lymph nodes.
Stage III:
Cancer has invaded nearby lymph nodes, but has not yet affected other parts of your body.
Stage IV:
Cancer has spread to distant places, such as other organs, such as your liver or lungs.