By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Brain cancer can originate from the brain cells themselves and can be the result of metastasis of cancer in other organs of the body. Cancer cells from other organs can spread anywhere throughout the body, including the brain, via the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Brain cancer or brain tumor is an abnormal growth in brain tissue.
Brain tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The tumor can either originate from the brain itself or come from another part of the body and spread to the brain (metastasis). A benign tumor does not contain cancer cells and often does not recur after removal. Most benign tumors do not invade the surrounding tissue.
A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells. Cells are the main building block of the body; They form tissues and organs. The body is constantly making new cells to help us grow, replace worn-out tissue, and heal injuries. Normally, cells reproduce and die in an orderly fashion, with each new cell replacing a lost one. However, sometimes the cells become abnormal and grow. In solid cancers, such as brain cancer, abnormal cells form a lump or mass called a tumor. In some cancers, such as leukemia, abnormal cells develop in the blood.
Carcinoma of brain cells can originate from somewhere other than the brain tissue itself and metastasize to the brain from other tissues. Brain tumors can be seen in the tissue of the brain, cerebellum, pituitary gland, medulla, meninges, brainstem, etc. Not all brain tumors are fatal. Even those that are malignant can be controlled and treated, of course, if they have not metastasized to the involved tissues. Although even if the brain tumor spreads and metastasizes to other tissues, if the treatment is done in such a way that all the parts are removed, the brain tumor will be controllable.
Brain anatomy and physiology: The human brain is the command center of the human nervous system. The brain receives input messages from the sensory organs of the body and sends output messages to the muscles. The basic structure of the human brain is similar to that of other mammals, but the ratio of brain size to total body size in humans is larger than that of all mammals.
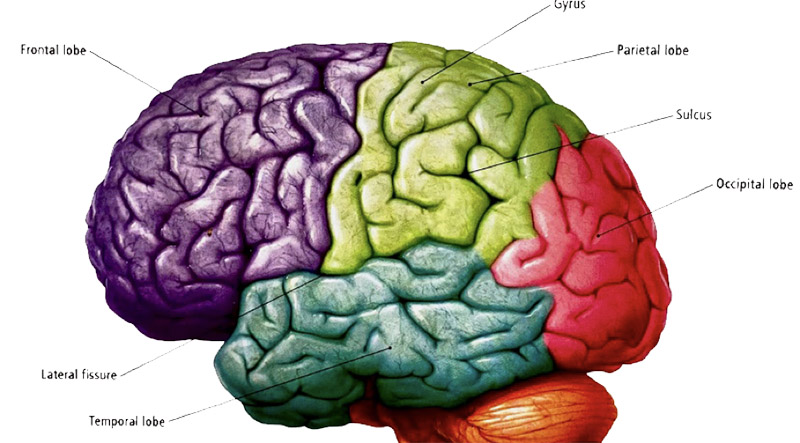
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain, which is divided into two hemispheres. Below it is the brainstem and behind the brainstem is the cerebellum.
The outermost layer of the cerebrum is the brain membrane, which consists of four lobes, including the anterior lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe.
Forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain: The human brain, like the brain of all vertebrates, consists of three main parts, the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Each of these three parts has fluid-filled cavities called ventricles. The forebrain becomes the cerebrum and its underlying structures. The midbrain becomes a part of the brainstem and the hindbrain will form the cerebellum and a part of the brainstem.
The cerebral cortex in the human brain has grown to a great extent and serves as the seat of complex ideas and emotions. Visual processing takes place in the occipital lobe near the back of the skull. The temporal lobe is responsible for sound and language processing and consists of the hippocampus and amygdala, which are involved in memory and emotions, respectively. The parietal lobe integrates input information from different senses and plays a very important role in spatial orientation and navigation.
Brainstem: The brainstem is connected to the spinal cord and includes the medulla, pons and midbrain. The most important functions of the brainstem include the exchange of information between the brain and the body, innervation from the brain to part of the face and head, as well as performing vital functions in controlling heart activity, breathing, and consciousness.
Thalamus and Hypothalamus: The Thalamus and Hypothalamus are located in the space between the cerebrum and the brainstem. The thalamus sends sensory and movement messages to the brain membrane and plays a role in regulating alertness, sleep and awareness. The hypothalamus connects the nervous system to the body’s endocrine system (which produces hormones) through the pituitary gland.
Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located below the cerebrum and has important functions in controlling body movements. The cerebellum plays an important role in the coordination and balance of the body’s organs, and in addition, it can also have cognitive functions.
The Role of the Brain: The brain is the most complex organ of the human body, which is usually referred to as the command center of the body. It monitors voluntary activities such as talking or making decisions, as well as automatic tasks such as blood circulation and heart rate.
Risk Factors of Brain Cancer:
* Family History
Only 5-10% of all cancers are hereditary. It is rare that genetic inheritance is the cause of brain tumor. If several members of your family have brain tumors, consult your neurologist. The neurologist will refer you to a genetic counselor.
* Age: The risk of most types of brain tumors increases with age.
* Race: In general, brain tumors are more common among white people. However, meningioma is more likely to occur among African-Americans.
* Exposure to Chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those you deal with in the workplace, increases your risk of developing brain cancer.
* Exposure to Radiation: The risk of brain tumor is higher among people who have been exposed to ionizing radiation. You may be exposed to this radiation through radiation therapy for another cancer. Atomic fallout also exposes you to radiation. Fukushima and Chernobyl nuclear accident are examples of exposure of people to ionizing radiation.
Brain Metastasis: Brain metastases are the most common types of brain tumors in adults. These metastases originate somewhere other than the brain and are transported to the brain through the blood. The most common origin of these tumors is lung, breast, skin, and with less prevalence, kidney cancer or colon cancer. In fact, brain metastases are tumors that first occur in tissues and organs outside the brain. Then they reach the brain through the blood and cause illness or death in people.
Types of brain tumors: Brain tumors can be classified based on different criteria, the most famous of which is the classification according to whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Another type of classification of brain tumors is based on the origin of the tumor, whether the main origin of the tumor is the brain tissue itself or it has metastasized to the brain from other tissues. But the most basic classification of brain tumors, which is also used in the clinic, is the classification based on the degree of aggressiveness. Based on this, tumors are divided into 4 grades or classes, with grade 1 tumors being the least dangerous and grade 4 tumors being the most dangerous.
Primary brain tumors: Primary brain tumors are those tumors that originate from the brain tissue itself. Their origin is astrocyte, oligodendrocyte, microglia, etc. Their origin is different in children and adults, such that in adults it originates from the anterior two thirds of the brain, while in children it originates from the posterior cranial cavity. The most famous of these types of tumors are glioma, meningioma and pituitary adenoma.
Secondary brain tumors: Secondary brain tumors are tumors that originate somewhere other than brain tissue. These types of tumors are initially formed in other parts of the body and then enter the lymph or blood stream and finally reach the cranial cavity through blood vessels and blood flow, where they grow and form a secondary tumor. Secondary brain tumors are much more common than primary tumors and are usually observed when a person has one of the other types of cancer and has metastasized and is incurable in the final stages of cancer. Secondary brain tumors usually originate from kidney, intestine and lung tissue.
Malignant tumors: Tumors are also divided according to whether they are benign or malignant. Malignant tumors have rapid and uncontrollable mitotic divisions and are constantly growing and dividing more. Anaplasia is another characteristic of malignant tumors. The term anaplasia means the unique appearance of brain tumor cells. These cells typically have a large nucleus, so that the volume occupied by the nucleus and cytoplasm is in some cases 1:1 ratio. Brain tumor cells can also be multinucleated.