By: Prof. Dr. Seyed Saeid Zamanieh Shahri, MD and Prof. Dr. Sonia Sayyedalhosseini, MD
Skin Cancer:
The skin is the widespread organ of our body and is also called the body membrane. This covering organ does its best to protect all the internal organs of our body from all external factors. The skin is more exposed to sunlight, heat, infection, cuts, burns and bruises than other organs. For this reason, there is a possibility of skin diseases. The skin is also a place to store water, fat and vitamin D. The skin has two inner and outer layers; The top layer is visible to the eye and the inner layer is not visible. This top layer is always exposed to all kinds of damage. One of the most severe injuries that can cause irreversible damage to the skin, is skin cancer. Sometimes the skin of the body changes its tissue and malignant cells form in the skin tissue. These cells can cause cancer in this part of the body. Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancerous) cells form in the skin tissues. There are different types of cancer, which start in the skin. Skin exposed to sunlight can increase the risk of non-melanoma skin cancer and active keratosis; Non-melanoma skin cancer and active keratosis often appear as a change in the skin. Tests or methods that examine the skin are used to diagnose non-melanoma skin cancer and active keratosis. It affects some specific factors (probability of recovery) and treatment options. The skin is the largest organ of the body that protects it from heat, sunlight, damage and infection.
Anatomy and physiology of Skin:
The skin, the largest living organ in the body, is in fact one of the most complex, interesting and prolific organs. The achievements and researches done in the field of recognizing the structure and function of the skin in the body during the last decade have been more and more effective than the series of studies of the last two centuries.
Skin functions:
Skin protects body against mechanical damage, heat and intense light radiation.
Prevents the penetration of chemicals and the entry of microbes and microorganisms into the body.
Excretes some harmful substances resulting from metabolic activities in the digestive system and liver.
Preserves hormones and enzymes inside the body.
As an external tactile organ, it transmits sensory messages through the nerves to the brain and nerve centers.
With the help of Langerhans cells (Immune System Cells), it plays an important role in the immune system.
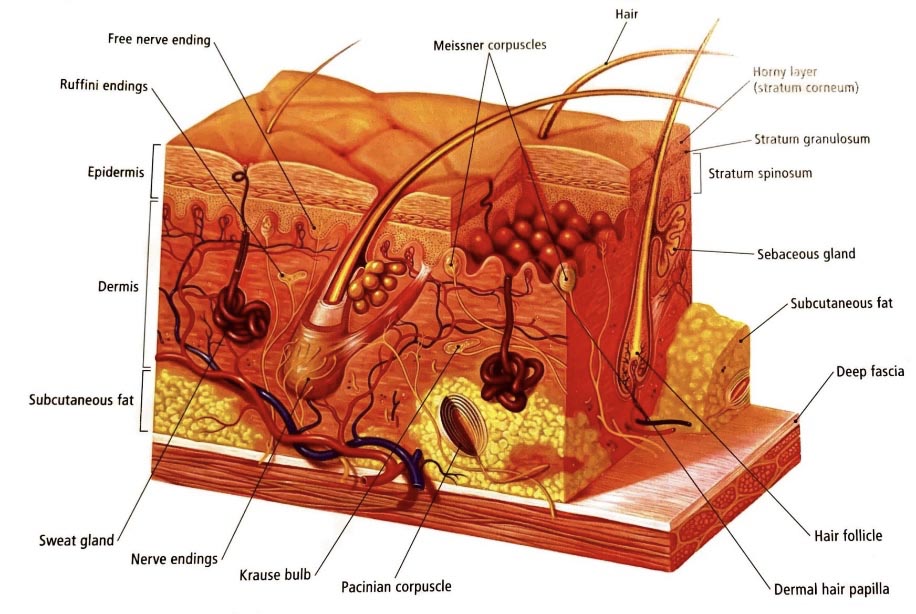
Skin components and structures:
In every square inch of skin, with a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm, several components can be seen that cooperate amazingly all together. 650 sweat glands, 65 hair follicles, 19 yards of delicate blood vessels, thousands of tactile cells, nerve endings, and Langerhans cells per square inch of skin, plus melanocytes and tyrosinase (melanin-producing) enzymes.
There are generally two types of glands inside the skin:
۱) Sebaceous glands
۲) Sweat glands
Usually the opening of each sebaceous gland opens to a hair follicle, but in some cases there are several sebaceous glands at the foot of each hair follicle that cause sebum to accumulate on the skin.
The sweat glands are deeply rooted inside the subcutaneous layers (dermis) in the form of spring-shaped terminals that pass through a hollow tube to expel sweat from the upper layers (epidermis) and its small opening opens at the surface of the skin.
Sweating does not clean the skin, but it is the exit of impurities through the small opening.
Men and women skin differences:
Human bodies are generally very similar and differ only in minor cases. Skin is no exception. Gender is the most important factor in making a difference in the skin.
Male gonadal secretions increase the thickness of the skin and the strength of the dermis layers.
Men’s skin is fuller and rougher than women’s skin.
Men have more sweat glands than women.
There is more melanin in men’s skin cells, which is why men’s skin is often darker than women’s.
Men’s skin is more greasy due to the production of more secretions by the sebaceous glands.
Chemicals secreted by the female glands make the skin smoother and softer.
Women’s body hair is shorter and thinner than men, but their hair can grow longer in length.
Men have more hair loss than women. In old age, parts of men’s hair fall out and the rest turn white or gray.
Race has very little effect on human skin and the only difference is the scattering of glands inside the skin. Dark color refers to certain cells in the skin that are almost the same number in all humans. In some breeds, the cells are larger and produce more melanin.
Other factors such as hair color and skin softness are inherited.
Risk factors for Skin Cancer:
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma include: Exposure to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight (including tanning) over a long period of time.
Other risk factors include:
Soft skin that has freckles, and burns easily, does not tan or is little dark.
Blue or green eyes or other colored eyes.
Blonde or red hair.
Having active keratosis.
Having a weak immune system.
Having specific changes in genes associated with skin cancer.
Exposure to arsenic.
Types of skin cancer:
Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three types of cells:
Flaky cells: Thin, smooth cells that make up the top layer of the epidermis.
Stem cells: Round cells are below the scaly cells.
Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis.
Melanin is a type of pigment that gives skin its natural color. When the skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes produce more pigment and darken the skin. Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but often the face, neck, hands and arms are exposed to sunlight.
There are different types of cancer that start in the skin. The most common types are stem cells and squamous cells which are non-melanoma skin cancers; Non-melanoma skin cancer rarely spreads to other parts of the body. Melanoma skin cancers is a very rare skin cancer and is more likely to invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Keratosis is a skin disease that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Hereditary skin cancer:
Skin color and exposure to sunlight can increase the risk of non-melanoma skin cancer and active keratosis. Anything that increases the risk of getting the disease is dangerous; but having a risk factor does not mean you will get cancer; Not having no risk factors does not mean you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk.